Abstract Author: Bao Hua Wang Weitao Chenxue Wei Zhang Zhong Yan Zheng Zhou shore / Zhengzhou Institute of abrasive grinding abrasive Ltd. mandatory national standards National Abrasives National Center for Quality Supervision and Inspection machine Seiko Co. recently released a summary of GB2494 & m
Author: Bao Hua Wang Weitao Chenxue Wei Zhang Zhong Yan Zheng Zhou shore / Zhengzhou Institute of Abrasives Grinding Abrasives Co., Ltd. National Quality Supervision and Inspection Center for State Machine Seiko Co., Ltd.
Abstract The latest mandatory national standard GB 2494—2014 “Consolidation Abrasive Safety Requirements†is implemented on January 1, 2015. The content of this standard is compared with the replacement standard GB 2494—2003 “General Abrasives Safety Rulesâ€. dramatic change. This paper first compares the differences between the new and old standard technical content, and then introduces and interprets the main technical contents of the new standard GB 2494-2014 "Consolidation Abrasive Safety Requirements", and finally explains the precautions for the implementation of the new standard. . In this way, the relevant parties are guided to correctly understand and implement the mandatory national standards.
Consolidated abrasive tools are grinding tools for grinding and cutting various metal and non-metal materials. They are widely used in machinery, automotive, aerospace, marine, electronics, geology, metallurgy, construction, petroleum, food processing, etc. The field is an indispensable tool in industrial production and plays an important role in the development of the national economy. Since the fixed abrasives are mostly used under high-speed rotation, once they are broken during use, the light equipment damages the equipment, the personnel are injured, and the heavy machine is destroyed. The quality of the products directly affects the people's lives. And property security, so the world has always attached great importance to the safety of bonded abrasives, and with the development of high-speed, high-precision and high-efficiency grinding technology, safety issues are more prominent, so China, Europe and the United States and other developed countries are National standards for the safety requirements for bonded abrasives have been developed. GB 2494 is currently the only mandatory national standard for the abrasives industry in China.
The original national standard GB 2494—2003 “General Abrasives Safety Rules†only stipulates the maximum working speed, acceptance, storage, installation, use and safety requirements for the used equipment. The content is relatively simple and lacks systematicity. The European standard EN 12413 "Consolidation Abrasive Safety Requirements" and the American National Standard ANSI B7.1 "Safety Requirements for the Use, Storage and Protection of Grinding Wheels" provide a more comprehensive and systematic definition of information on bonded abrasives, including safety. Various technical requirements and testing methods, signs, use information and other content. Among them, the content of American standard technology is very detailed, but the scope is more general, and it is quite different from China's standard system. Relatively speaking, the European standard has the highest working speed, safety system, lateral load capacity, size limit, limit deviation and round runout tolerance, static unbalance quantity, signage and usage information, etc. depending on the type of equipment and the type of application. The content has been scientifically and reasonably regulated, providing comprehensive safety requirements for the designers, manufacturers and users of the abrasive tools to reduce the risk, and the technical framework is basically consistent with the Chinese standard system.
Since there is no international standard for the safety requirements of bonded abrasives, there is no international standard for the revision of the national standard GB 2494. The newly revised national standard GB 2494—2014 “Consolidation Abrasive Safety Requirements†is based on the European and American standards, and is based on the technical system of the European Standard EN 12413 “Consolidation Abrasive Safety Requirementsâ€, combined with the actual industry in China. The relevant technical content is determined by the situation and technical level.
We have carried out a comparative analysis of the technical content of the new national standard GB 2494-2014 "Consolidation Abrasive Safety Requirements" and the original national standard GB 2494-2003 "Ordinary Abrasives Safety Rules", and the new standard GB 2494-2014 "Solid" The main technical contents of the Safety Requirements for Grinding Tools were introduced and interpreted. At the same time, the problems that enterprises should pay attention to when implementing the new standards were elaborated.
Comparison of GB 2494 new standard and original standard technical content
The technical content of the new mandatory national standard GB 2494-2014 "Consolidation Abrasive Safety Requirements" and the original national standard GB 2494-2003 "Ordinary Abrasives Safety Rules" are shown in Table 1.


It can be seen from Table 1 that the technical content of the new standard is not only stipulated in the content of the content, but also the content of the specific terms is more perfect than the original standard.
I. Terms and definitions
In addition to the terms and definitions specified in GB/T 16458 and GB/T 17588, the terms and definitions of the relevant grinding equipment, grinding methods and application types are specified in the standard.
The terms and definitions of the relevant grinding equipment specified in the standard are given in Table 2. The terms and definitions of the relevant grinding methods and application types are shown in Table 3.
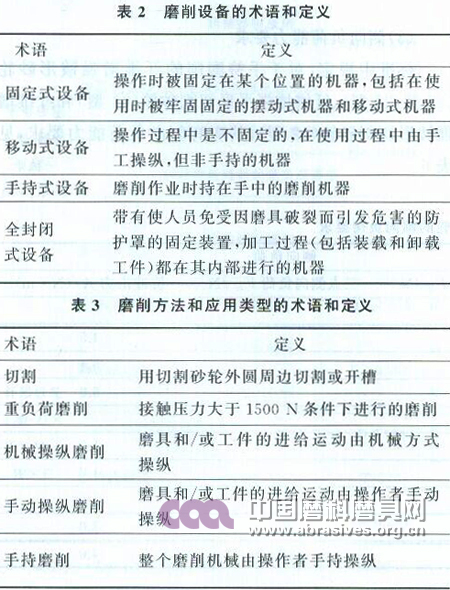
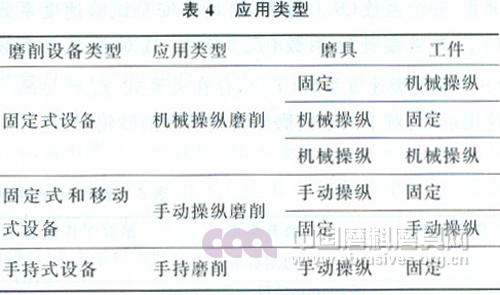
Standard users should be familiar with and understand the above terms and definitions and the list of application types, because the safety factor, safety speed and safe speed test coefficient, rupture speed and rupture speed test coefficient, highest work in the standard "safety technical requirements" section Speed ​​requirements are tied to specific application types. If you do not understand this part, you will not be able to correctly understand and master the relevant content in the "Safety Technical Requirements".
In addition, the relevant symbols and abbreviations and their definitions are given in the standard, such as maximum allowable speed, maximum working speed, safety test speed, safety test speed coefficient, rupture speed coefficient, rupture speed, minimum rupture speed and so on. This article does not introduce much about this.
Second, safety technical requirements
1. The highest working speed design rules
The standard stipulates that the abrasive tool should meet the principle of being able to withstand the expected external force and load when in use, and be designed and manufactured according to the highest working speed of the following range:
<16-16-20-25-32-35-40-45-50-63 (or 60)-70 (or 72)-80-100-125 in m/s.
According to this regulation, when designing abrasive tools or manufacturing abrasive tools, the maximum working speed should be selected from the above speed series, and other speed values ​​should not be selected. For example, a manufacturing company can produce a grinding tool with a maximum working speed of 50 m/s, and the maximum working speed of the product should not be nominally 48 m/s or 51 m/s.
2. Strength requirements
(1) Grinding tool (without handle with grinding head) requirements for swing strength
The standard stipulates that the rotational strength requirements of abrasive tools (without shank grinding heads) include safety speed requirements and rupture speed requirements. To this end, the safety factor of the grinding tool (without the shank grinding head) and the safety test speed coefficient and rupture speed coefficient associated with it are given in the standard. The specific values ​​are shown in Table 5.
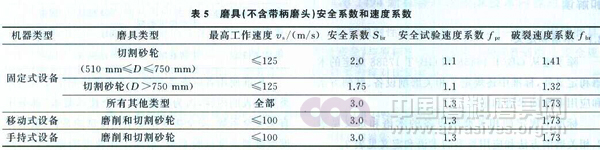
It can be seen from Table 5 that the safety factor (Sbr) of the corresponding abrasive tools is different for different machine types, different abrasive types, different maximum working speeds, and different safety factors (Sbr), corresponding safety test speeds. The coefficient (fpr) rupture velocity coefficient (fbr) is also different. In general, the larger the safety factor (Sbr), the greater the safety test speed coefficient (fpr) and the rupture velocity coefficient (fbr) of the abrasive tool; and the relationship between the safety factor (Sbr) and the rupture velocity coefficient (fbr) Fbr=Sbr. Application example: For the grinding wheel used in the fixed grinding machine, the safety test speed coefficient is 1.3 and the rupture speed coefficient is 1.73 for the grinding wheel. For the fixed cutting device, the cutting wheel with the outer diameter D=1250mm is used. When the swing strength is detected, the safety test speed coefficient is 1.1 and the burst speed coefficient is 1.32.
For the test method of the swing strength, the standard stipulates that the fixed abrasive tool should be installed on the grinding wheel rotary test machine in accordance with GB/T 2493 for inspection. Among them, for the safe speed test, the speed should be gradually increased to the test speed for 30s. For the rupture speed test, the rotational speed should be gradually increased to the minimum rupture speed; if the fixed abrasive reaches the minimum rupture speed without rupture, it is qualified; at the same time, all the fixed abrasives subjected to the rupture speed test should be destroyed. In this regard, the abrasive manufacturer should pay special attention to the fact that the bonded abrasives that have passed the rupture speed test must not be sold or put into use because the inside of the abrasives is likely to have been damaged and there are safety hazards.
( 2). Rotor strength requirement with handle
The shank with a shank shall have a safety factor of Sbr = 3.0 at the highest working speed to prevent cracking caused by centrifugal force. The shank with shank should have a safety factor of Sab=1.3 to prevent deflection and give an example of its maximum allowable slewing speed in the form of an appendix (informative).
(3). Lateral load capacity requirements
The standard stipulates that for hand-grinding fiber-reinforced é’¹ type grinding wheels (type 27, type 28), fiber reinforced flat-shaped cutting wheels (type 41) and fiber reinforced circular cutting wheels (type 42), it should have lateral load capacity. Requirements, see Table 6.
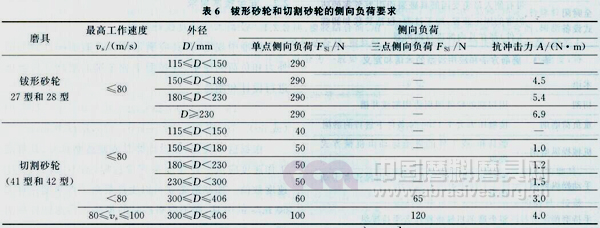
In the standard preface, the lateral load capacity requirement is a recommended requirement, not a mandatory requirement. This is mainly due to the fact that the current lateral load capacity test equipment has not been mass-produced locally. With the mass production of test equipment, this clause will become mandatory.
3. Size limit and maximum working speed
The standard specifies the maximum working speed of the abrasive tools for different machine types, different application types, different size limits, different bonding agent types, and is divided into general requirements and special requirements. Due to the large shape of the abrasive tools and the length of the paper, the paper does not list them one by one. Only two typical shapes, the flat grinding wheel and the cup grinding wheel, are introduced. See Table 7. Other details should be consulted in the standard text.
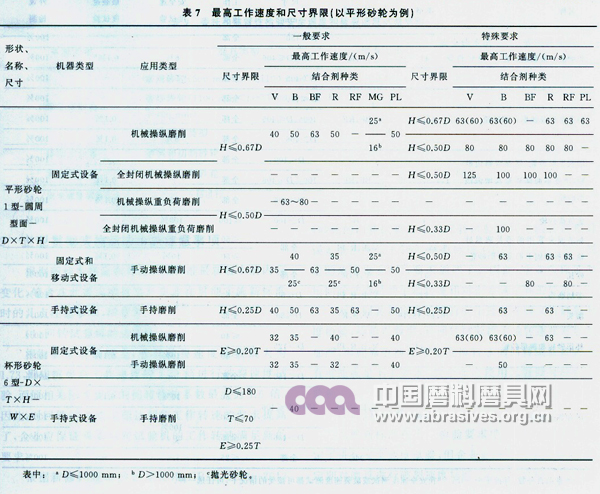
When designing and manufacturing abrasive tools, the highest working speed in the general requirements is usually used, and the highest working speed in special requirements is used when it is used for special purposes. Moreover, the designed and manufactured abrasive tools must meet the maximum working speed requirements in Table 7, and must not be lower than the specified value. For the flat grinding wheel, if it is used on a fixed grinding machine or mechanically operated, the size limit is H≤0.67D (such as D=750mm, H=305mm grinding wheel), the bonding agent is V, the maximum working speed is the normal use. Should be 40m / s, and can not be lower than this speed (if not 35m / s); the same is a flat grinding wheel, if it is used on a fixed grinding machine, manual grinding, the size limit is H ≤ 0.67D (such as D = 750mm , H=305mm grinding wheel), the bonding agent is V, for normal use, the maximum working speed should be 35m / s, but not lower than this speed (if not 32m / s). For the example grinding wheel, the maximum working speed is 40m/s when designed and manufactured, which is suitable for both mechanically operated grinding and manual-operated grinding.
For the cup-shaped grinding wheel (in addition to the bowl shape, the dish shape and the two-sided concave No. 2 grinding wheel, etc.), the bonding agent is V, for general use, and its maximum working speed is 32 m/s. The maximum working speed specified in the original standard GB 2494-2003 is 30m/s. Therefore, in the future, the design and manufacture of such grinding wheels should meet the new requirements. When designing and manufacturing abrasive tools, the dimensions must also be met. This actually contains two layers of meaning: (1) meets safety requirements. For example, the flat grinding wheel is generally H≤0.67D, the heavy-duty grinding is H≤0.50D, and the hand-grinding is H≤0.25D. In fact, it is required to have sufficient broadband on the end face; as well as a cup-shaped grinding wheel, fixed equipment E≥ 0.20T, handheld device E ≥ 0.25T, in fact, the thickness of the hole is required to be sufficient. Otherwise the safety of the abrasive tool cannot be guaranteed. (2) Differentiate the shape. For example, the cylindrical grinding wheel should be W<0.17D, otherwise it will become a flat grinding wheel (H≤0.67D); if it is a flat cutting grinding wheel, it should be T≤0.02D, otherwise it is not a cutting wheel (41 type), but a flat shape Grinding wheel (non-cutting, type 1).
Other requirements in the safety technical requirements include appearance, allowable imbalance, and signs. The content is easy to understand and should not be explained too much.
Third, the inspection rules
Factory inspection rules
The standard specifies the grinding tools with different names, different shape types and different bonding agents, and the minimum detection percentage of the safety test, the rupture speed test and the appearance inspection of the inspection items at the factory inspection under different size ranges and different maximum working speeds. See Table 8. The remaining items should comply with the provisions of JB/T 10450.
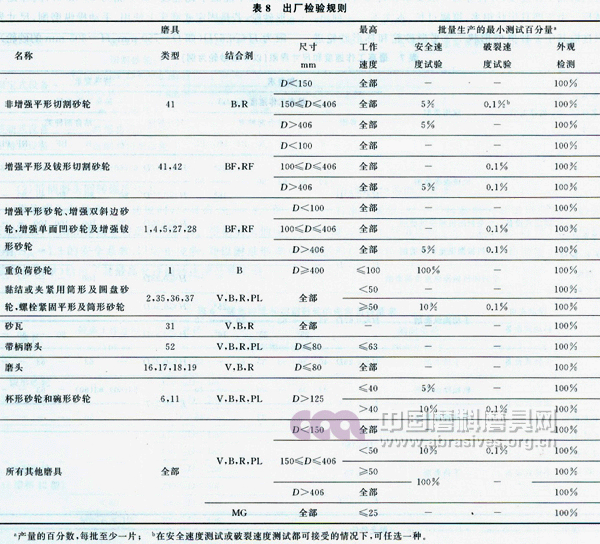
It can be seen from Table 8 that regardless of the type of abrasive tool, its appearance should be 100% tested at the factory inspection. For safe speed tests or rupture speed tests, different abrasives specify a minimum percentage of the corresponding sampling, but at least one per batch; and in the case where both are acceptable, one of them may be selected. For example, for a fiber-reinforced resin flat-shaped cutting wheel (type 41, bonding agent BF), if the outer diameter D < 100 mm, the rotation strength test is not performed; if the outer diameter is 100 mm ≤ D ≤ 406 mm, at least 0.1% is taken for the breaking speed. Test; if the outer diameter D> 406mm, at least 5% should be taken for safe speed test or at least 0.1% for rupture speed test. For example, for a ceramic flat grinding wheel (type 1, binding agent V- corresponds to one type included in the name column "all other abrasive tools" in Table 8), if the outer diameter D < 150 mm, the turning strength test is not performed; If the diameter range is 150mm≤D≤406mm, then the maximum working speed is divided into two cases: one is that for the highest working speed Vs<50m/s, at least 10% should be taken for safe speed test or at least 0.1% for cracking. For the speed test, the other is that for the highest working speed Vs≥50m/s, the safe speed test should be carried out 100%; if the outer diameter D>406mm, the safe speed test should be carried out at 100.
2. Entrustment and supervisory inspection
The test rules for the safe speed and rupture speed of abrasive tools during commissioning and supervisory inspection are specified in the standard, see Table 9. At the same time, the remaining requirements are specified in accordance with the provisions of JB/T 10450.
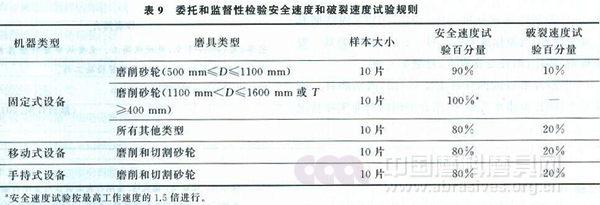
The rest, such as the acceptance and storage, installation and use of the same provisions as the original standard, will not be repeated here, but standard users should be aware of the relevant content.
According to the new standard regulations and the changes in the content of the latest version of the relevant reference standards, the author hereby points out the precautions for the implementation of the new standards by the abrasive manufacturing enterprises for reference.
1. Applicability of the rotary test machine
According to the new standard, the maximum rupture speed coefficient of the grinding tool is 1.73, that is, the rupture speed test should be carried out at 1.73 times of the maximum working speed, and the slewing test coefficient specified by the original relevant standard is 1.6 times maximum. Therefore, the requirements for the working speed that the rotary testing machine should be able to achieve are improved, and the company should ensure that the working speed of the rotary testing machine used meets the new requirements.
According to the newly revised national standard GB/T 2493-2013 "Spin test method for grinding wheel", the relative error range of the spindle speed of the rotary test machine is ±1.5%, while the range specified by the original standard GB/T 2493-1995 is ±3. %, the request is tightened. Therefore, the company should ensure that the relative error of the spindle speed of the rotary testing machine used meets the new requirements.
Since the rotary strength test has both a safe speed test and a rupture speed test, the test coefficient is large, and the relative error of the rotary test machine spindle speed is tightened. Therefore, the rotary test machine that changes the rotational speed by changing the pulley is likely to fail to meet the requirements, so the enterprise A stepless speed swing tester should be used.
2. Swing strength test
Although the new standard only requires the safety speed test for some abrasive tools in the factory inspection requirements, the enterprise should regularly test the rupture speed of the abrasive tools during the actual quality control, and should be in the new product development and new formulation test. When the new process test, raw material changes and equipment conditions change, the rupture speed of the grinding tools is tested, so that we can do our best to ensure the safety of the produced abrasive tools. In addition, only this can ensure that the inspection is qualified at the time of entrusted inspection and supervised inspection, because the entrusted inspection and the supervised inspection basically include both the safe speed test and the rupture speed test.
3. Lateral load capacity
Although the new standard's requirements for lateral load capacity are recommended, it does not mean that the company may not perform lateral load capacity quality control, because the reference standard JB/T 1045 "Consolidated Abrasives Inspection Rules" has been revised. It will be released, and the factory requires inspection of the lateral load capacity of the grinding wheel. Therefore, enterprises that produce fiber-reinforced enamel grinding wheels (type 27, type 28) and fiber-reinforced cutting wheels (type 41, type 42), if they do not have lateral load-capacity testing methods, they should submit samples at regular intervals according to standard requirements. The unit of the corresponding detection capability (such as the testing organization) performs such project testing.
Conclusion
1. Mandatory National Standard GB 2494-2014 "Consolidation Abrasive Safety Requirements" Compared with the original standard GB 2494-2003 "Ordinary Abrasives Safety Rules", the content changes greatly and is more perfect.
2. The new standard is based on the technical system of the European standard EN 12413 "Consolidation Abrasive Safety Requirements", and the relevant technical content is determined based on the actual situation and technical level of the industry in China.
3. Enterprises should improve the testing methods according to the requirements of the new standards, and implement quality control according to the standard requirements to ensure product quality and safety.
The Xunda Liquid Adhesive is recommended to use only Xunda coating systems. The liquid adhesive systems consist of butyl based polymeric resins dissolved in an organic solvent system.
The liquid adhesive provided high cohesive between pipe surface and the coating system.
It can be used by hand brush or machine spray application.
We also provide the solid primer ,the solid primer should dissolved in an organic solvent and stirred before application.
Liquid Adhesive
Liquid Adhesive ,Liquid Glue,Clear Liquid Glue,Liquid Nails Adhesive
Jining xunda pipe coating materials co., ltd. , https://www.pipeanticorrosion.com