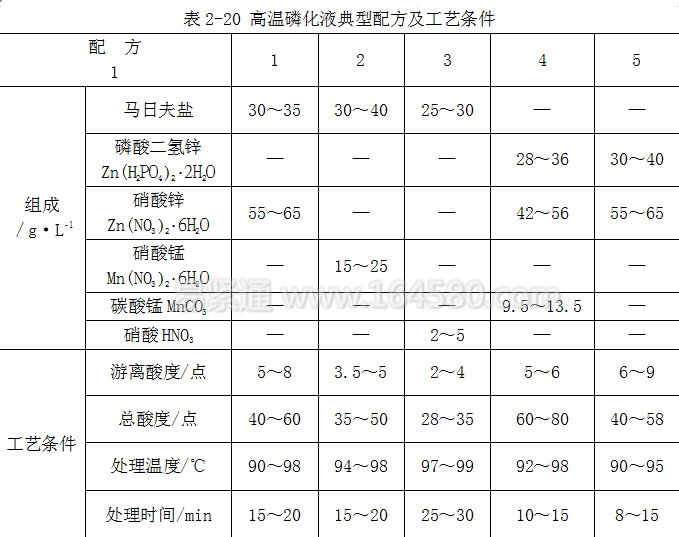
High-temperature phosphating solution formula and process conditions The temperature of high-temperature phosphating treatment is 80-90~C, the treatment time is 10-20 min, and the phosphating liquid-acid ratio is 7-8. The film obtained by high-temperature phosphating treatment has strong corrosion resistance and good bonding force, but the heating time is long, the temperature is high, and the volatilization amount of the solution is large, resulting in unstable acidity and uneven crystallinity of the film layer. Several typical formulations and process conditions for high temperature phosphating solutions are shown in Table 2-20.
The temperature and phosphating treatment temperature of the medium temperature phosphating solution is 50-75 ° C, the treatment time is 5-15 min, and the phosphating liquid acid ratio is 10-15. The free acidity of the medium temperature phosphating is stable, the operation is simple, the phosphating time is short, the production efficiency is high, and the corrosion resistance of the phosphate film is good. The typical formulations and process conditions of the medium temperature phosphating solution are shown in Table 2-21.

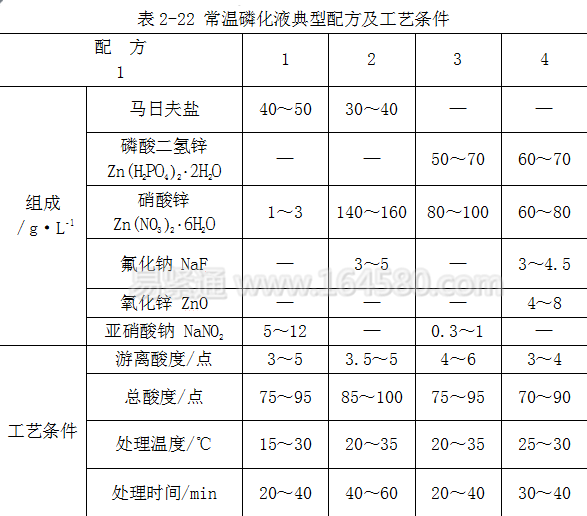
Normal temperature phosphating solution formulation and process conditions The temperature of the normal temperature phosphating treatment is 15-35 ° C, the time is 10 ~ 60 min, the phosphating liquid acid ratio is 20 ~ 30, the normal temperature generally does not need heating, can be carried out at room temperature, The phosphating solution is relatively stable, but the processing time is relatively long and the production efficiency is low. Several typical formulations and process conditions of normal temperature phosphating solution are shown in Table 2-22.
Phosphating process In general, the phosphating process of steel parts mainly includes pre-treatment, surface adjustment, phosphating and post-treatment. The specific steps are: pre-treatment (deoiling and degreasing → hot water washing → cold water washing → pickling) Descaling → cold water washing → surface adjustment → phosphating → cold water washing (sealing → cold water washing → deionized water washing) → drying.
(1) Degreasing by oil. Degreasing is one of the key processes in the entire process. The presence of oil stains will seriously affect the formation of phosphating film, and even the formation of phosphating film, and also affect the quality and corrosion resistance of phosphating film, which should be highly valued. Therefore, the grease on the surface of the steel workpiece should be removed before phosphating.
Degreasing methods mainly include organic solvent degreasing, lye degreasing, acid degreasing, electrochemical degreasing, surfactant degreasing, ultrasonic enhanced degreasing, carbon dioxide degreasing, drum degreasing, flame burning degreasing, etc. Physical and chemical degreasing methods. When degreasing, different methods should be used depending on the material of the workpiece and the degree of surface oil stain.
The lye degreasing mainly relies on the chemical action of the lye to remove the grease and dirt on the surface of the workpiece to achieve the purpose of purifying the surface of the workpiece. This method is suitable for steel and some metals that are not susceptible to lye corrosion (such as nickel, copper, etc.). Alkaline degreasing has the characteristics of low cost, non-toxicity and simple operation, and has been widely used. However, the degreasing of lye has the disadvantages of long oil removal, unsatisfactory degreasing effect, and strong corrosiveness and serious back alkali. It has been rarely used at present and is only used as primary degreasing. It is now usually cleaned with a multi-component degreaser.
Several degreasers are provided for the oil stain on the surface of steel, copper, aluminum and their alloys, as well as the non-metallic surface oil stains such as rubber and glass. The formulations are shown in Table 2-23.
After the degreasing is finished, remove the workpiece from the degreasing tank and rinse it off with running water or high pressure water.
(2) Pickling and rust removal. After degreasing, the surface of the workpiece should be cleaned of rust and scale, otherwise it will affect the uniformity of the growth of the phosphate film and reduce the quality of the film. There are many methods for surface descaling, such as chemical immersion method (acid rust removal method), ultrasonic method, electrochemical method, sand blasting method, shot peening method, high pressure spraying method, manual method, and the like. When removing rust, the most effective method can be selected according to the type of workpiece material and the surface rust layer to ensure the normal operation of phosphating.
The main mechanism of pickling and rust removal is to use chemical solution such as acid to chemically react with rust and oxide on the surface of the workpiece to produce soluble or insoluble metal salts, thereby achieving the purpose of rust removal. The formula and process conditions of pickling and rust removing liquid are shown in Table 2-24.
(3) Surface adjustment. The surface adjustment is abbreviated as the surface adjustment. This process has been widely used in recent years. It mainly means that the workpiece is immersed in the surface conditioning solution for several minutes before phosphating, and taken out and immediately immersed in the phosphating bath for phosphating. The purpose is to cover the surface of the workpiece with a layer of activation center to facilitate the deposition of phosphate on the surface of the workpiece; in addition, the acidity of the surface of the workpiece can be adjusted to make it in the best state of film formation, which is favorable for uniform and compact phosphating. Phosphating film. The main component of the surface conditioning liquid is titanium oxysulfate, pyrophosphate, sodium phosphate, etc., and the content is 1 Torr. ~10‰.
(4) Phosphating. Phosphating refers to the process of immersing a workpiece in a phosphating solution prepared according to the required ratio and forming a phosphate film on the surface after a period of treatment.
(5) Post-phosphating treatment. Phosphating post treatment is also called passivation, and its main purpose is to improve the performance of the phosphating film. When phosphating is carried out directly after electrophoretic coating or other rust prevention and painting, the passivation treatment may not be performed. Phosphating membranes have different uses and post-treatment methods are also different. For example, for cold-deformed machining and friction-reducing workpieces, the workpiece can be immersed in a lubricant such as a hydrazine or soap.
In order to improve the corrosion resistance of the phosphating film, a method of immersing vegetable oil or mineral oil is generally used, and a sealing treatment with a dilute solution of citric acid or chromate may be used to reduce the pore area of ​​the film and improve the corrosion resistance of the film. The formulation and process conditions of the phosphating membrane sealing solution are shown in Table 2_25.
Table 2-25 Formulation and process conditions of phosphating membrane sealing solution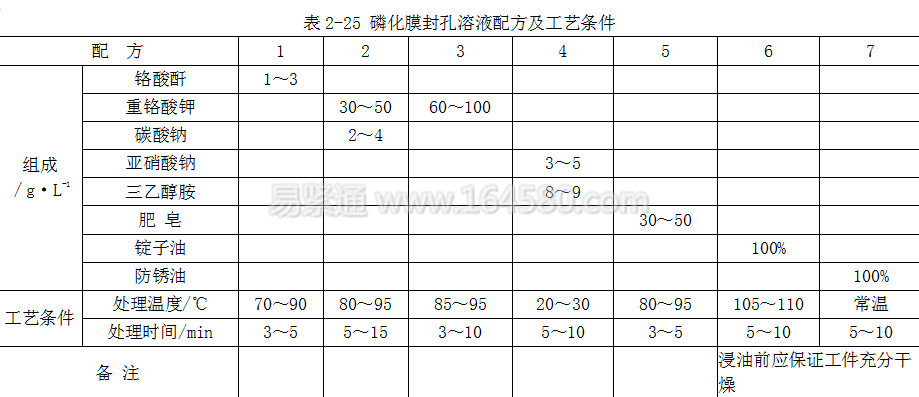
1) The chromate solution is closed. The working environment of most steel equipment or parts is more complicated. In order to protect it from corrosion, it can be protected by phosphating film. In order to reduce the pores of the phosphating film and improve its corrosion resistance, after the film layer is dried, it is subjected to a sealing treatment with a dilute solution of chromic acid or chromate. The specific ratio can be 0.015% of cr6+/Cr3+=3 chromic acid solution, or phosphoric acid can be added in the solution according to the ratio of CrO3/H3PO4=5.
The concentration of chromic acid should not be too high. When the concentration of chromic acid exceeds 0.05%, the corrosion resistance of the phosphating film can only be slightly improved. When the concentration of chromic acid is higher than 0.2%, the dissolution of the phosphating film is caused. In addition, if the sealing liquid contains impurities, it will cause local corrosion on the surface of the steel workpiece and reduce the corrosion resistance of the film layer. Therefore, the sealing liquid must be prepared with deionized water.
2) Oil immersion is closed. After phosphating of steel, the film should be immersed in oil after it is completely dried to close the pores of the phosphating film. When the mineral oil is used for sealing, an appropriate amount of corrosion inhibitor can be added.
3) Paint is closed. Coating the phosphatized film with resin paint or nitrocellulose lacquer can strengthen the protection of steel workpieces, and its corrosion resistance is ten times higher than that of pure phosphating film. The painted film can be naturally dried. When drying in an oven, the temperature should be controlled according to the specific application requirements of the coating.
4) The soap is closed. When the phosphate film is used for cold deformation processing and for reducing the surface wear of the friction member. The post-treatment of the phosphating film should be closed with soap liquid to improve the lubricity and wear resistance of the phosphating film and prevent the film and metal: surface strain and cracking. The easiest and most effective way is to immerse in a potassium soap solution. In this solution, the surface film of the phosphating film will be converted into potassium soap, the concentration of potassium soap solution is 10 ~ 30g / L, the acidity can be adjusted with sodium carbonate solution, the working temperature of the solution is 50 ~ 70 ° C, the immersion time is generally It is 4 to 6 minutes.
320W Solar Panel,Mono Cell Solar Panel,Trina Mono Solar Panels,335W Solar Panel
Zhejiang G&P New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.solarpanelgp.com