Water pollution has increasingly become one of the major problems of global environmental problems, in which pesticide, medicine, cosmetics and other organic pollutants are especially difficult to treat. At present, one of the most commonly used methods to remove organic compounds in industrial waste water is activated carbon adsorption. This method has some problems: 1 slow adsorption rate; 2 for relatively hydrophilic organic pollutants removal effect is not obvious; 3 activated carbon regeneration requires a lot of energy consumption, higher, and after regeneration after the adsorption effect. The fruit will also be reduced.
Water soluble polymer beta cyclodextrin seems to be a good new choice. Cheap and continuous glucose supermolecule macromolecules are used to adsorb organic compounds. The principle of the adsorption of organic pollutants by beta cyclodextrin is to form a host guest molecule with organic matter. The adsorption rate constant for a variety of organic pollutants is 15-200 times that of activated carbon. After flushing under mild conditions, it can be reused many times without reducing the performance. Compared with commercially available activated carbon materials, Beta Cyclodextrin Polymers exhibit better performance in the removal of organic pollutants in real environments. The material can be used not only in domestic water filtration, but also for industrial wastewater treatment and ecological restoration. It will be very likely to replace activated carbon as the next generation of new water treatment materials.

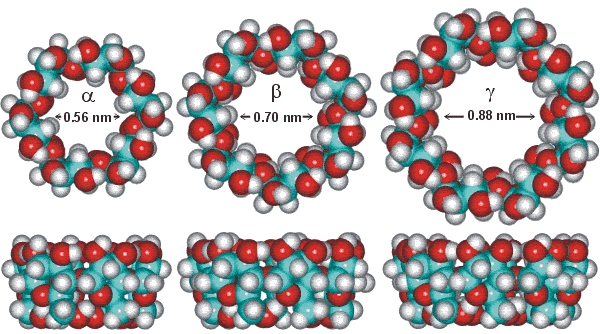
Natural Cyclodextrins
The most common cyclodextrins are alpha, beta, and gamma cyclodextrins having six (α), seven (β), or eight (γ) anhydroglucose units in the ring structure. Among them, beta Cyclodextrin is mostly common used.
Different sizes lead to different physicochemical characteristics for the respective molecules:
|
Characteristics |
Alpha (α) |
Beta (β) |
Gamma (γ) |
|
Number of glucose units |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
Molecular weight |
972 |
1135 |
1297 |
|
Water solubility(g/100ml), 25° C |
14.5 |
1.85 |
23.2 |
|
Cavity diameter (nm) |
0.57 |
0.78 |
0.95 |
|
Height of torus (nm) |
0.78 |
0.78 |
0.78 |
Chemically modified Cyclodextrins
Cyclodextrins can be modified by various procedures such as:
Substituting one or more hydrogen atoms in the primary and/or secondary hydroxyl groups (esters, ethers, glycosylcyclodextrin)
Substituting one or more primary and/or secondary hydroxyl groups
Chemically modified Cyclodextrins (CDM's) exhibit substantially increased aqueous solubility with concomitant retention of the inclusion complexing properties of the starting Cyclodextrin. They therefore appear to offer specific applications within various industries, such as foods, pharmaceuticals, personal care/cosmetics, diagnostics, etc. Hydroxyalkyl b Cyclodextrins such as Hydroxypropyl b Cyclodextrin are examples of those chemically modified Cyclodextrins.
Natural Alpha Beta Gamma Cyclodextrin
Natural Beta Cyclodextrin,Natural Alpha Cyclodextrin,Natural Gamma Cyclodextrin
Zhiyuan Biotchnology , http://www.zycydextrin.com