Overview
Ammonia and ammonia nitrogen are crucial components in the nitrogen cycle of aquatic systems, playing significant roles in the growth of aquatic plants, the health of aquatic organisms, and overall water quality. This article delves into the basics of ammonia and ammonia nitrogen, their impacts on human health and the ecological environment, and the importance of monitoring these parameters for effective water management and pollution control.

Â
What is Ammonia?
Ammonia (NH3) is a form of nitrogen that is readily absorbed by aquatic plants and incorporated into proteins, amino acids, and other essential molecules. While ammonia is essential for plant growth, high concentrations can promote excessive algae and aquatic plant growth. Bacteria present in water can convert ammonia into nitrates (NO3-) through a process called nitrification. This process consumes dissolved oxygen, which is crucial for aquatic life.
Â
Understanding Ammonia Nitrogen
Ammonia nitrogen refers to the combined nitrogen present in water in the form of ammonia (NH3) or ammonium ions (NH4+). This form of nitrogen is a nutrient that, in excess, can lead to eutrophication of water bodies. Eutrophication is a process where excessive nutrients promote algae growth, leading to oxygen depletion and harm to aquatic life. Ammonia nitrogen is a primary oxygen-consuming pollutant in water and is toxic to fish and other aquatic organisms, posing a threat to ecosystems and human health.
Â
Impact on Human Health
Ammonia nitrogen in water can be converted into nitrite under certain conditions. Prolonged consumption of nitrite-contaminated water can lead to the formation of nitrosamine, a potent carcinogen that is extremely harmful to human health. Therefore, monitoring ammonia and ammonia nitrogen levels in water is crucial to ensure the safety of drinking water and protect human health.
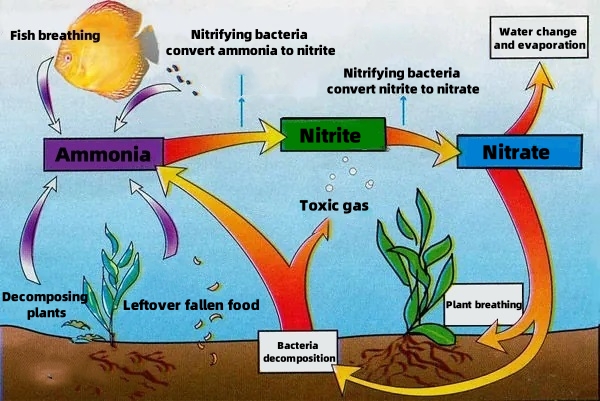
Â
Importance of Monitoring Ammonia and Ammonia Nitrogen
Monitoring ammonia and ammonia nitrogen levels is essential for several reasons:
- Protecting Aquatic Life: High levels of ammonia nitrogen can be toxic to fish and other aquatic organisms, disrupting ecosystems and impacting biodiversity.
- Preventing Eutrophication: Excessive nutrients, including ammonia nitrogen, can lead to eutrophication, which depletes oxygen levels and harms aquatic life.
- Ensuring Drinking Water Safety: Monitoring these parameters helps ensure that drinking water is free from contaminants that may pose a risk to human health.
- Supporting Water Management Decisions: Data on ammonia and ammonia nitrogen levels can inform water management decisions, such as treatment processes and discharge regulations.
How to Measure Ammonia and Ammonia Nitrogen in Water
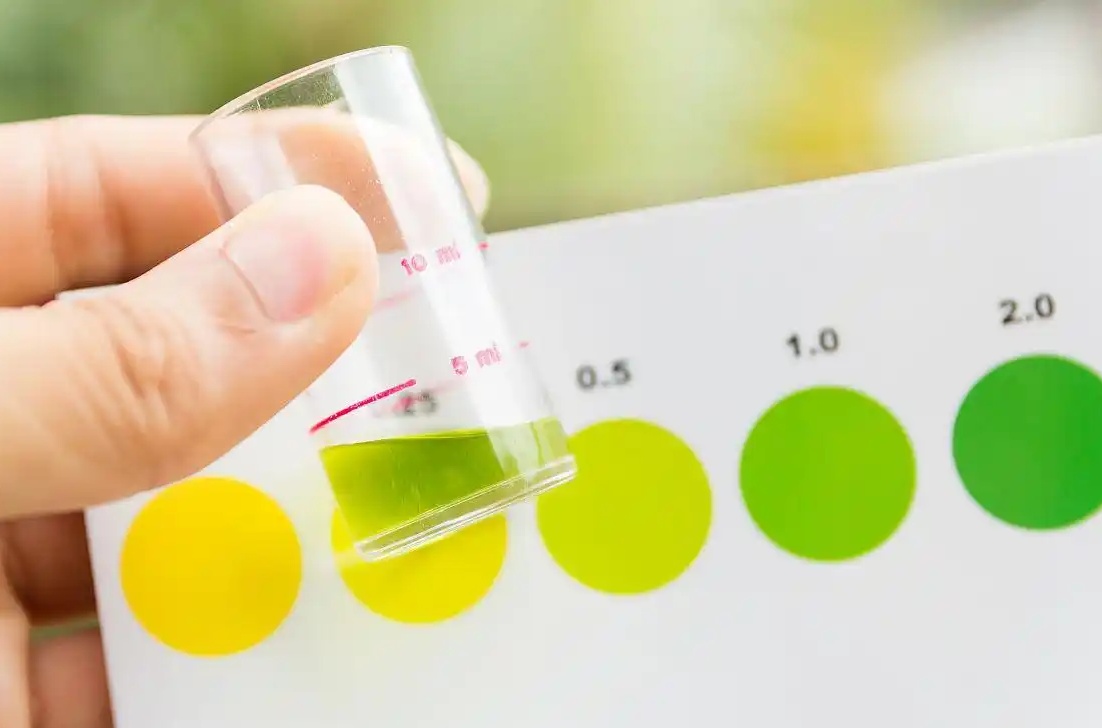
Measuring ammonia and ammonia nitrogen levels in water involves using specialized instruments and techniques. These measurements can be conducted in the field or in a laboratory setting, depending on the specific needs and requirements.
Field instruments are portable and designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, providing accurate readings even in challenging environments. Laboratory-based systems, on the other hand, offer higher precision and are ideal for research and quality control applications.
Choosing the right measurement system involves considering factors such as the measurement environment, additional parameters that need to be measured, and data collection needs. Continuous monitoring systems can provide real-time data, allowing for the detection of trends and changes in water quality over time.
Â
Conclusion
In summary, ammonia and ammonia nitrogen are critical parameters for assessing water quality and ensuring the health of aquatic ecosystems and human populations. Monitoring these parameters helps identify potential pollution sources, support water management decisions, and protect both aquatic life and human health. By understanding the basics of ammonia and ammonia nitrogen and their impacts on the environment, we can take steps to mitigate their effects and preserve the quality of our water resources.
Ammonia,Ammonia Nitrogen,Nitrogen Cycle,Eutrophication
Suzhou Delfino Environmental Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.daruifuno.com