 The year 2010 is the last year of the "Eleventh Five-Year Plan" and is also the year for making decisions on the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan". Under the background of the international political and economic game, Greece triggered the European debt crisis and the global economic turmoil. The central government has tried to reverse the “crisis†of the domestic economy by transforming it into an “accident†through restructuring macroeconomic policies such as preventing inflation, expanding domestic demand, and adjusting the structure. During the period, in order to stimulate the economic recovery, Tiancai Bank's credit inflows into the market, leading to a rapid increase in the prices of necessities for residents, mainly agricultural products, resulting in a high CPI. At the same time, the latest round of quantitative easing monetary policy in the United States has led to a further increase in global liquidity, and China is facing a huge pressure on capital inflows. It is not difficult to find the shadow of hot money behind some of the skyrocketing prices this year. In May this year, the State Council issued the "Circular on Further Enlarging Work to Ensure the Implementation of the "Eleventh Five-Year Plan" for Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction Targets" and strictly control the new projects of the "two highs" and overcapacity industries, to a certain extent, to curb the excesses of the previous period. Continue to grow blindly.
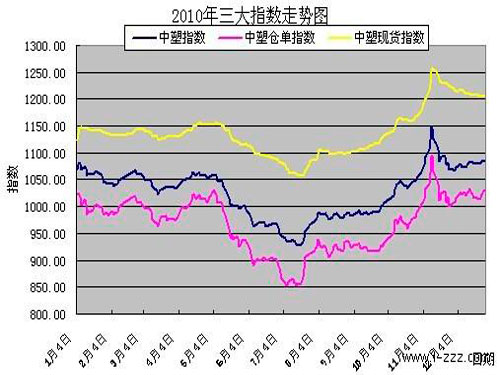
The year 2010 is the last year of the "Eleventh Five-Year Plan" and is also the year for making decisions on the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan". Under the background of the international political and economic game, Greece triggered the European debt crisis and the global economic turmoil. The central government has tried to reverse the “crisis†of the domestic economy by transforming it into an “accident†through restructuring macroeconomic policies such as preventing inflation, expanding domestic demand, and adjusting the structure. During the period, in order to stimulate the economic recovery, Tiancai Bank's credit inflows into the market, leading to a rapid increase in the prices of necessities for residents, mainly agricultural products, resulting in a high CPI. At the same time, the latest round of quantitative easing monetary policy in the United States has led to a further increase in global liquidity, and China is facing a huge pressure on capital inflows. It is not difficult to find the shadow of hot money behind some of the skyrocketing prices this year. In May this year, the State Council issued the "Circular on Further Enlarging Work to Ensure the Implementation of the "Eleventh Five-Year Plan" for Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction Targets" and strictly control the new projects of the "two highs" and overcapacity industries, to a certain extent, to curb the excesses of the previous period. Continue to grow blindly. Under this background, the domestic plastics market generally showed a scene of icy and heavy weather. In the first half of the year, due to the European debt crisis, and the impact of domestic tightening policies introduced by the domestic market, coupled with the decline in the cost of crude oil and other related raw materials, the petrochemical inventories were high. In the second half of the year, under the impact of a large amount of liquidity, the global economy has recovered to a certain degree, but the accompanying inflation has also caused related raw materials. The currency attributes have emerged, and the plastics market has oscillated upward trend under the supply and demand side and the financial side. As of December 28, the China Plastics Warehouse Receipts Index closed at 1031.9 points, an increase of 18.07 points or 1.78% from 1013.83 points at the end of the previous year. The PP warehouse receipts index closed at 1200.46 points, up 31.02 points from the previous year's 1169.44 points, or 2.65%; the LLDPE warehouse receipts index closed at 1020.48 points, down 157.31 points from the previous year's end of 1177.79 points, a decrease of 13.36%.
The warehouse receipts index oscillating pattern in January-April, which has repeatedly been affected by the highs of last year and blocked, at the same time China's GDP reached a high point in the first quarter, followed by continued decline, the return of the May Day holiday, the warehouse receipt index began for two months The decline, which PP warehouse receipts index by May 4 (the central bank raised the deposit reserve ratio for the third time in the year the highest rate) 1961.11 points fell to the lowest of 981.57 points on July 6, the cumulative decline of 17.94%. LLDPE warehouse receipts have shown signs of weakness from the beginning of the year, falling from the highest of 1188.56 points on January 7 to the lowest of 871.35 points on July 19, with a cumulative drop of 26.7%. Since then, with the gradual digestion of the European debt crisis, the international financial environment has begun to stabilize. Under the support of a series of economic data, US stocks and crude oil began to rebound. China’s resumption of exchange reforms enhance exchange rate flexibility and is considered as a global economy. Towards a part of recovery. After constructing a small double bottom in July, the index ushered in a wave of larger rebounds. The PP warehouse receipts index rose from the lowest of 981.57 points on July 6 to the highest of 1285.36 points on November 11, with a cumulative increase of 30.95%. The rebound has been a new high since the end of 2008. The LLDPE warehouse receipts index rose from the lowest of 869.11 points on July 19 to the highest 1149.99 points on November 11 with a cumulative increase of 32.32%. Among them, the US launched the second quantitative easing policy on December 3rd as a turning point. Due to the expectation of hot money impacting the domestic capital market, the index has risen rapidly. However, due to the effective handling of the central government, hot money is entrenched in Hong Kong, India, and Southeast Asia and other places are afraid to shake. The expectation that hot money will impact the domestic market will be greatly reduced, and the warehouse receipt index will quickly slump, and it should properly return to the level before QE2 came out. However, after more than a month of shock consolidation, the central bank raised interest rates by 25 basis points from December 26th. The impact of hot money is expected to once again touch investors' nerves, but the real economy is also being suppressed by the rate hike. Under the leadership of this long-short two factors, the index at the end of the year showed upward pressure.
2011 is the first year of the “Twelfth Five-Year Planâ€, and it is also the key point for China’s economic and social development to gradually enter the mid-transition period. Under the background of deepening transformation, China’s economy will show a pattern of high growth and high inflation in 2011. It is expected that China's economic growth rate will be 9.6% next year, and the inflation rate will be 3.7%. The main driving force for growth comes from transitional investment. The inflation level will rise significantly under the double superimposition of transitional price increases and excess liquidity. Adding interest rate increases at the end of the year will surely make the international hot money more influx into mainland China. In terms of production capacity, energy-saving emission reductions and power cuts will, to a certain extent, weaken the imbalance between supply and demand brought about by excess production capacity. In addition to the related raw material costs, plastic prices are expected to rise steadily in the coming year.